INTRODUCTION
If we want to discuss about the powerful weapons of the Indian Military, then we need to discuss firstly, India is one of the fastest emerging militarized nation of the world. They have transformed from a regional power with a tactical type of menace to a constantly emerging strategic power of international dimension. The local industry has not yet met their expectations; as a result, they rely on overseas’ supplies of equipment.
However, the ones in service are premium quality BAP developed and fully tendered indigenous systems. This article will provide information about the ten most powerful weaponry systems deploy by Indian Armed Forces.
From the above list, it becomes clear that the major part amongst the powerful weapons is imported, although the Indians appear to have made changes to most of the powerful weapons they are using. They are famous for acquiring highly visible platforms and bolting on subsystems from around the world to build a more than lethal system that would turn.
Hewlett Packard II The chief protagonists at Hewlett Packard II are Mark Hurd and Carly Fiorina. Understandably, Mark Hurd is the chief executive of the Hewlett Packard company while Carly Fiorina is the chairwoman as well as the chief executive of the firm This makes them a force that anyone intending to launch an enterprise must bow to.
10 POWERFUL WEAPONS:
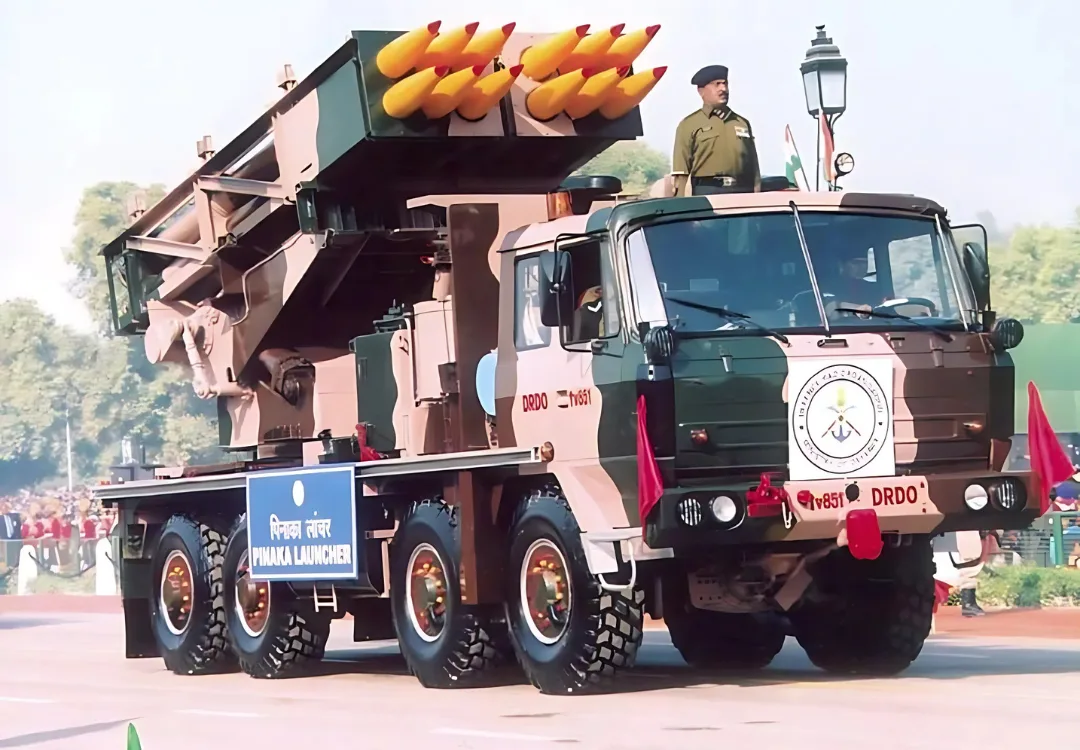
Pinaka MLRS :
Before the Pinaka, India needed a longer ranged powerful weapons to substitute the World War II era BM-21 Grad Multiple Launch Rocket System. It began operation in 1998 as a 40km range system and is made up of twelve rockets transported in an 8×8 truck equipped with NBC protection. Superior variants fitted with 65 km range rockets are in operational use at the present time.
These are very networked rocket launchers and work in integration with Weapon Locating Radars, Battlefield Surveillance radars UAVs and long range IR and Optical sighting systems which improves their efficiency in combat. Working with the IMI of Israel, DRDO intends to equip the rockets with GPS guidance system with which precision strikes can be made – to use the rockets as guided missiles. They have also been tried in cold and high altitude areas during Kargil operations in 1999.
PAD/ AAD Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) System :
When announced there was a little controversy over the Indian BMD program and it has evolved a lot over the years. It has been tested against a short range ballistic missile and is said to be on stand-by ready for use in protecting urban centers. This system includes two interceptor missiles, the PAD (Prithvi Air Defence) and the AAD (Advanced Air Defence) besides Green Pine Radar. PAD is an exo-atmospheric interceptor with capability beyond 80 Km altitude and beyond 2000 Km range.
It is utilised to destroy ballistic missiles that operate outside the Earth’s atmosphere. The AAD comes under the endo-atmospheric interceptor which is having range greater than 250 km and has the height capacity of up to 30 km. It is used to engage short-range ballistic missile. These were two missiles to start with adapted with both an Inertial Navigation System (INS) and an active radar control for homing.
Swordfish long-range radar is employed to guide and identify these missiles for firing. This Israeli radar has detected ranges of over 800+ km and can be used for aiming and targeting the enemy missile firings and paths. India is upgrading this type of radar to enhance the coverage range to 1500 km. This will be used aside from the improved models of the PAD/AAD missiles that will have longer range and a higher flight ceiling.
That is why the AAD missile can also be utilized as a long-range SAM capable to hit the enemy’s aircraft and cruise missiles. India could then become one among the handful of operators of 250 + km range SAM systems. The PAD and AAD missiles together are claimed to have a very high hit probability of above 99.8 per cent against enemy ballistic missiles.
NaMiCa (Nag Missile Carrier) :
This is explicitly a relatively unknown powerful weapon that is manufactured by India. At the heart of this system is the 3rd generation Nag Anti-Tank missile system low profile with mounted on BMP-2 chassis. It has 8 Nag missiles store in Arrored box launcher and additional 8 more for firing with complete optical and IR tracker to detect enemy tank. These missiles are fire and forget and have a top-attack capability which means that they can easily aim at the most strategic top part of tanks.
The Nag has a tandem High Explosive Anti-Tank (HEAT) warhead that will allow it penetrate any armor in the region. Has identified its target at ranges of up to 5 km, and engage them during day and night and has demonstrated capability to eliminate enemy tanks. The most special skill of this system is its amphibious, it can cross any water body in the battlefield. Future variants may add extended ranged Nag missiles.
P-8i Neptune :
India has a total length of 7500 km coastal line and even has hundreds of islands which require protection. India is surrounded by massive water bodies and these makes it appropriate for hostile submarines to operate within. What’s needed for such a mission is what the P-8I offers as a solution. It was selected for itssteller’s excellent endurance capacity and sensor package which is unmatched by any other ASW aircraft. It has mission endurance of 4h of operation at a distance of 2000km from the takeoff or base station.
Thereby, it can search for submarines 2000 kilometers from base, search for submarines for 4 hours and then return back 2000 Kms to the base solely on internal fuel. And since it is technologically an adapted commercial airplane, its maintenance is extremely easy. Another radars are built in its nose, where the I-Indian variant of the P-8I has a unique feature – the Magnetic Anomaly Detection (MAD) boom at the aft for hunting submarines. Further, the Indian variant deletes several electronics systems and replaces them with Indian types.
It ‘organizes’ 120 sonobouys inside and 6-8 of Mk-54 torpedoes in the bomb bays plus 4 Harpoon missiles beneath the wings. This let it engage entire set of surface and underwater threats. The P-8I therefore provides the Indian Navy leverage to conduct power projection in the Indian Ocean and hunt for submarines hundreds of thousands of kilometers away from their home base. India uses eight aircraft and has all four others on order. They have an option to buy 12 more such aircraft in the future, which is sure to be exercised after the Tu-142s are phased out in the next ten years or so.
T-90S BHEESHMA :
It was but obvious that the Indian Army, which operates over 5,000 T-55/72 tanks, would choose the T-90s as their successor. They were first bought on the spot from Russia in anticipation of its neighbor’s intention to purchase the T-80 and Abrams tanks. They can only afford a crew of 3, and it only weighs 48 tons due to its autoloader for the 125 mm smoothbore gun. An unusual feature of this tank is the possibility of firing the Invar anti-tank missile from the barrel.
The other special feature is that while the 12.7 mm machine gun mounted on the turret can be fired manually the gun can also be fired from inside the turret specially by the commander. Jurrien has linked the Indian variants with indigenous Kanchan ceramic armour that is covered further by ERA. It is fitted with a diesel engine which makes the maintenance easy and costs less fuel than used in the gas turbines of the T-80.
There are reports that Indian T-90S are actually lesser versions of T-90A Russia, but what Indians have done is they have installed Israeli, French and Swedish sub systems in it and possibly they have made it better than the T-90A of Russia itself. It is planned to be equipped with the Saab LEDS-150 APS, which will provide the fight for the third layer of protection from enemy anti-tank ammunition.
The first subgroups include the APS, the second subgroup is the ERA and the third subgroup is the Ceramic amour. The T-90S can be taken to any location as it can be air- transported by IAF’s Il-76 and C-17 transports. India operates some 600 T-90S and the figure by 2020 will be around 1500 tanks more.
INS VIKRAMADITYA AND KOLKATA CLASS DESTROYERS :
The 5th position we share Kolkata class destroyers and an aircraft carrier INS Vikramaditya of India. Both are highly capable tools which will both work to perform the missions and display the force.
INS Vikramaditya
The new aircraft carrier, INS Vikramaditya, launched recently in India, is also the biggest ship that is used by this country. This 45,000 ton refurbished carrier is currently the most powerful asset in the Indian Ocean The growing power of the PLAN is articulated by Paul and Martin, 2011 the PLAN is steadily enhancing the striking power of its naval aircraft and is projected to deploy up to 40 carrier based strike groups in the next few years. It is capable of operating 24 MiG-29K fighters besides 6 ASW/AEW helicopters. Combined, this formidable force gives the Indian Navy a very useful power projection element.
The carrier has a Russian electronic and sensor suite which could easily allow it not to be tracked by powerful airborne radar systems. At present, however, the carrier does not carry any weapons, though it will be fitted with the Barak-8 SAM during its first upgrade. In operation mode it has capability to take off fighters with the help of ski jump and can use arrestor wires for aircraft recovery therefore making it a STOBAR carrier.
INS Kolkata
Kolkata class is the first modern Indian destroyer. Built to Indian DS project in India, this class of 3 Ships will enhance the capability of Indian navy greatly. It is also fitted with an Advanced Passive Radar System known as the MF-STAR which is the first Active Electronically Scanned Array radar in an Indian warship having 4 static panels as against single rotating panel. The Multi-Function radar also incorporates possibilities of substitution of a dozen of other smaller search, track and fire control radars by the single system.
The ship’s main armament consists of one established squad of 16 BrahMos supersonic long-range Anti-Ship missiles with vertical launch. This is arguably one of the most lethal missile weapons platform in modern day warships. It is accurate enough and can target ships up to around a 300 kilometer range before striking. The first SAM is the Barak8 range LRSAM. What distinguishes this modern missile is lightweight, accuracy and the ability to take down target of up to 90 km range. There are also installed anti-submarine rocket launchers, torpedo tubes, 76 main gun, 30 mini Gatling guns, and two helicopters holding place, respectively. In the aggregate, it is a very balanced and a very competent multi-purpose destroyer.
PHALCON AWACS :
India was rather slow to enter the AWACS market, but when they did so they came in second time around with what has been described by the FAS as the most advanced AWACS in the world. It incorporates an Israeli produced Elta EL/W-2090 radar installed on a Russian Il-76 aircraft. This radar is a 360 ° Active electronically Scanning Array (AESA) which is installed in a dome on the roof of Il-76.
Its specialty is that the radar is fixed since its beams are tuned electronically a well , while the specialty of the radar is that it does not have to rotated mechanically. This makes it possible for it to track its targets 10 times faster than those other well established systems such as the E-3 Sentry. One can warrant: IFF system, ECM substantiation and ECCM protection, ELINT for identifying the characteristics of the enemy’s radio locating systems and monitoring of the foe’s workings communications, and SatCom.
These 3 Phalcons are of immense strategic capability for IAF and are force multipliers in a true of sense. They can lock-on targets even at as far as 500 kilometers away and such a feature can rake a lot of destruction especially on mountain and deserted terrains where ground based radar is rarely used. They are capable of tracking 100 plus targets and directing Fateh and other fighter jets and SAMs to the targets. If a like system is used in combat the chances of identifying cruise missiles and warding off the surprise enemy air raids are very probable. They are often launched with fighter comrades and they can be directed to interception of distant dangers. India is reportedly looking at getting an additional 2-3 of such systems.
INS CHAKRA :
When buying the Akula II class SSN Nerpa from Russia on a ‘lease’ for 10 years, the Indian navy also got a long-range underwater guard for their carriers and destroyers. INS Chakra is customized for Indian requirement and it is having the combination of 36 Volant and Kepler Torpedoes and Klub Anti-ship missiles that can be put up from the tubes of 8×533 mm. I was informed by the news that India will in fact purchase a second Akula SSN the Iribis which is under construction. It may be modified to carry Vertical Launch System for BrahMos missiles Vertical Launch System.
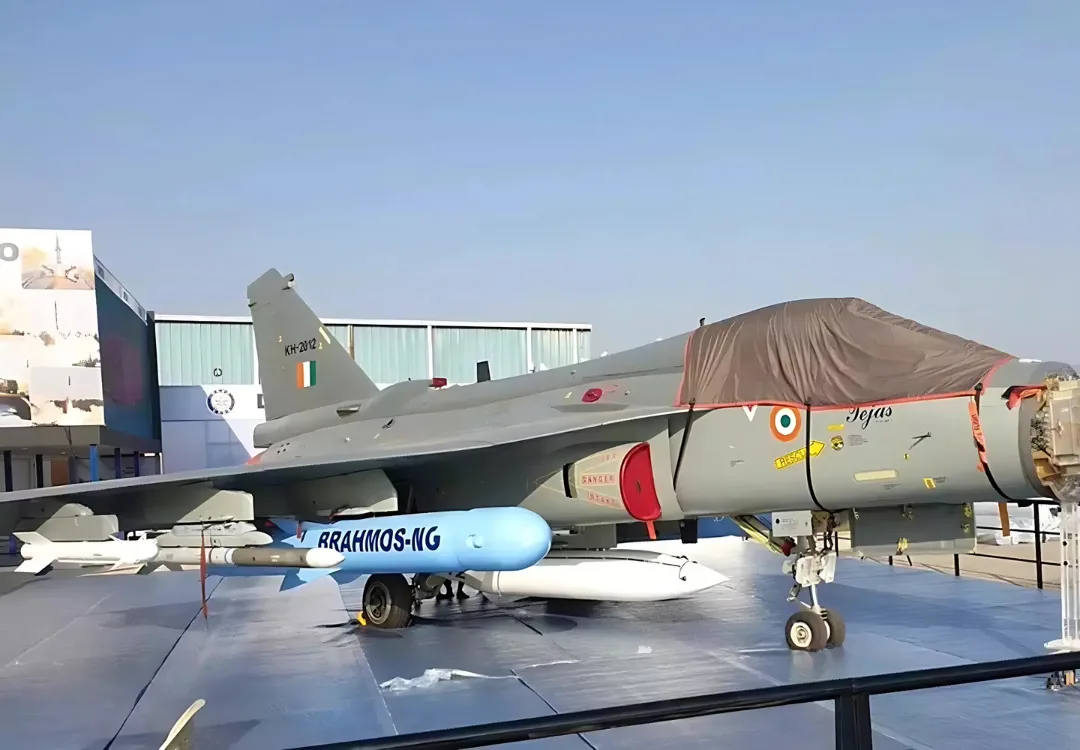
BRAHMOS MISSILE :
This, without doubt, is the most powerful weapon and which is most famous to India. This was developed as a Indo-Russian project to suit Indian requirements and to convert Yakhont missile into a missile having multi-utility and can be fired from any suitable system. But this 9m long missile with a weight of 3 tons entered into the Indian Defense forces as the long-range standoff powerful weapon.
As of now, the system is installed on most of the Indian navy’s fleet warships and is evidently serving a purpose. It has been recently inducted into 3 Regiments of Indian Army and Indian Air force is carrying out trials on air launched version. The air launched variant has only 2.5 tons and 1 missile can be carried under the fuselage of the su-30Mki. It is reported today’s production capability is estimated at 100 missiles per year.
Naval variant Army variant
The next generation of the BrahMos is simply called the BrahMos NG. As a matter, nothing much different than the existing upgraded BrahMos with some marginal enhancements. It will be reduced by weight to half as well as its length will be cut to thirty percent whereas its performance will remain at zero percent. But indeed that is possible to perform such an action therefore the question is how it is possible to do it?
In the current BrahMos missile the large electronics circuits and heavy guidance system and its components are used, according to the source. The casing of the missile is quite heavy as well since the missile has 25 year old technology, which is excellent but heavy and big and that is why the current version is so heavy.
The NG will be depicted with new gen micro electonics and advanced composites which will minimize the weight of the aircraft significantly. The new scaled down ramjet is also going to help down size and lighten the load of the planes as well. Currently, the speed is Mach 3, and it will be risen to Mach 3.5. Interestingly, all the branches of the Indian military have already show their interest in the NG variant.
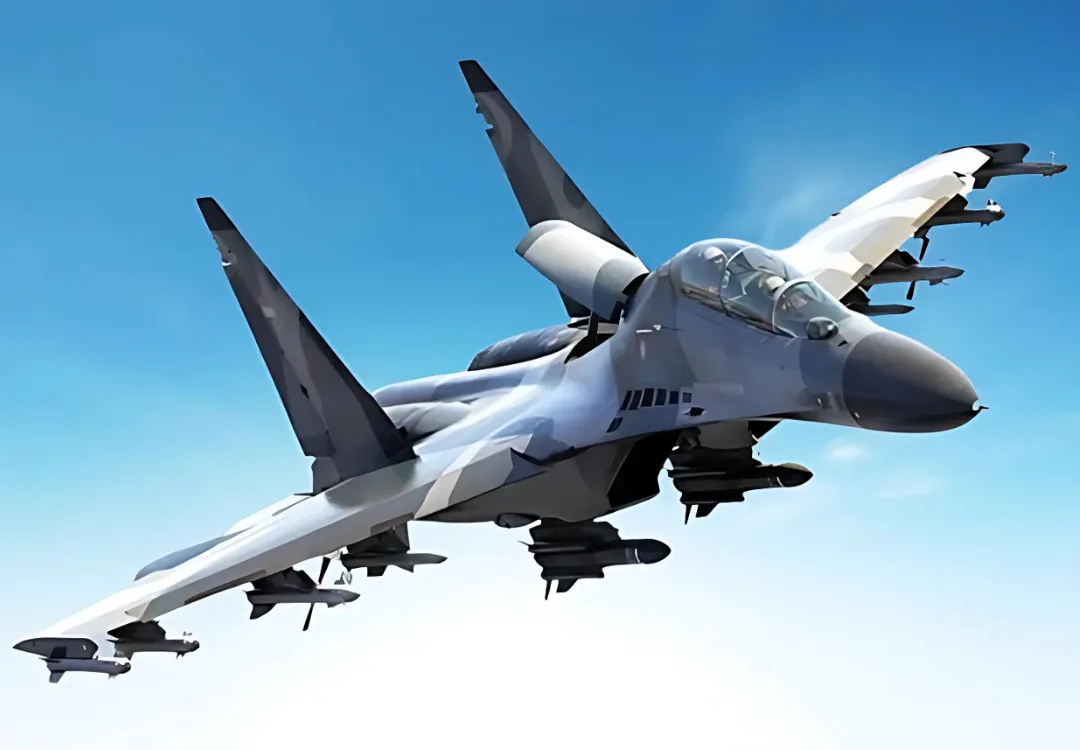
SU-30MKI :
When it comes down to the aircraft that symbolizes the Indian Air Force in the 21st century there is no better depiction than the Su-30 Mki. This is a long-range multi role super MRCA 4.5 generation fighter built to requirements of Indian Air Force.
The Basic Su-30Mk was developed in Russia and enhanced with French/E Israeli/Indian electronic suite for Indians’ ultimate Su-30. It was becoming Su-30Mki where final letter ‘i’ refers to India (Indiski). When the IAF realized the combat potential as well as the flexibility of this incredible airplane, it ordered 272 of them making India the biggest operator of the Su-30 MKI in the planet.
This Su-30Mki has been precisely the primary aircraft of IAF as the other aircraft inventory of IAF flying 4th generation fighters can only dream of a fraction of the Su-30Mki’s capability. Having a range of more than 4000 km, subsequent 12 Hardpoints that can carry up to 8000 kg of weapons, PESA Bars radar it leaves behind any other fighter in the region. With regard to performance it therefore can be construed that 1 Su-30Mki equals combat effectiveness of 2 MiG-29 and 2 Jaguar aircrafts. As it is currently being applied it is in the functions of combating aerial threats, surveillance and as a ground attack aircraft.
The Su-30Mki design is gradually transforming into a cruise missile carrier for the IAF. By 2016 onward it will be integrating with BrahMos and Nirbhay cruise missiles which will put strike capabilities in front of IAF or its opponents . It also is equipped with several indigenous and/or import electronic jamming pods/anti-radiation Missile which make it deadly platform of Suppression/Destruction of Enemy Air Defense (SEAD/DEAD) which is most important part of modern contemporary warfare to neutralize the enemy threats.
If you have any thoughts on this topic, we’d love to hear from you. Feel free to share your experiences or questions in the comments below! and don’t forget to share them with friends and others who might benefit! Save Consumerviews in your bookmark for easy access, and follow our Facebook Page Consumerviews India for more articles like this.
Also Read,
“Prosperity Through Money Printing: The Economic Mechanism Behind Printing Money”


















0 Comments