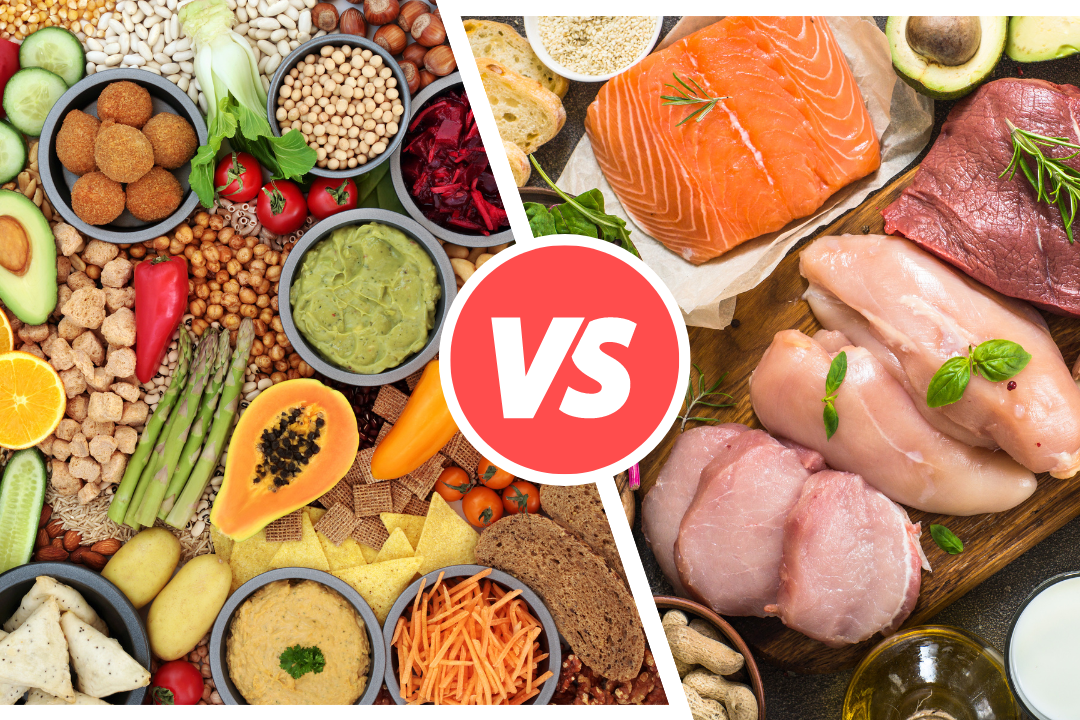
Introduction to Plant Protein vs Animal Protein
Plant protein vs animal protein is one of the main themes of the discussions going on in the recent past around the world regarding diets. Thus, an understanding of the type of proteins and the way towards choosing the right source is crucial when trends are leaning towards awareness of nutrition and sustainability. Animal proteins and plant proteins are both different, with positives and negatives in each of them. Here, users get a detailed understanding of plant protein and animal protein, which enables them to select a proper diet.
Plant Protein vs Animal Protein
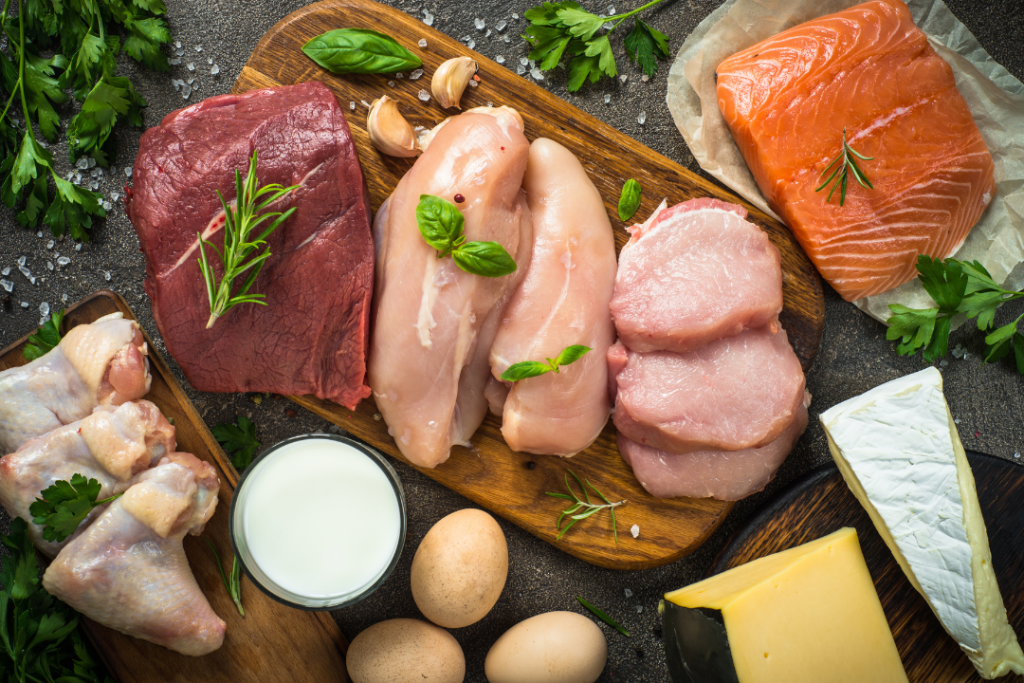

Introduction to Protein Sources
Protein is one of the essential macromolecules that contribute to the formation of tissues as well as to the execution of tasks in various organs. They are derived from amino acids, as they make up proteins, some of the most critically important biomolecules. Knowledge of the source of these proteins can go a long way in influencing your health, nutrition and even the state of the environment.
Amino Acid Profiles
Proteins are made up of amino acids and based on the appropriateness of the amino acids in the body, they are categorized as essential or non-essential. Condimental amino acids do not get manufactured in the human body, and they have to be ingested through foods. Thus, most of the meat-bearing animals’ proteins have all ten amino acids, which classify them as complete proteins. However, majority of plant protein are incomplete proteins that lack one or more of the essential amino acids.
Bioavailability and Digestibility
Bioavailability, on the other hand, describes the amount of nutrient that gets into the circulation and is thus available to do its action. Proteins from animals normally are considered to have better bioavailability than proteins from plants. That is why animal proteins are erectile mechanism and are easier for the body to digest and utilize. Nevertheless, there is about 90% of proteins in soy and 87% in quinoa, which are of high bioavailability.
Nutrient Density
Protein, which is obtained from animal products like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products is recognized as a source of some essential nutrients and these include Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, iron, and zinc. As per the nutrient density, these are sometimes even less available in plant-based sources or are present in fewer amounts. On the other hand, consumption of plant protein sources is associated with certain advantages, such as fiber, antioxidants, and different beneficial phytochemicals.
Advantages of Plant Protein for Health
Heart Health
Proteins derived from plants have been greatly attributed to helping in the cardiovascular health of consumers. Plant proteins help to decrease cholesterol and the probability of heart diseases if taken as part of a plant-based diet. Products like beans, lentils, nuts, etc offer good protein but no fat, that is accompanied by most animal protein.
Weight Management
Plant proteins are arguably more beneficial, especially concerning weight management, because proteins that come from plants contain significantly more fiber than those that come from animal-based products. As such, fiber makes an individual consume less food in a given period, hence reducing the overall food calorie intake. This can be of particular interest, especially to individuals who are in desperate need of either maintaining or losing some weight.
There are challenges in plant-based protein, to learn more read Obstacles and Overcoming Critical Hurdles with plant based proteins.
Digestive Health
The fiber present in plant proteins plays a key role in the digestive tract by ensuring that people do not suffer from constipation. It can also result in an improved composition of the diverse microorganisms in the digestive system, thereby contributing positively to human health.
Cancer Prevention
Some of the proteins in plants are antioxidants with phytochemicals that have the potential to lower the incidence of cancer. These compounds assist in the reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation signs, which are associated with cancer formation.
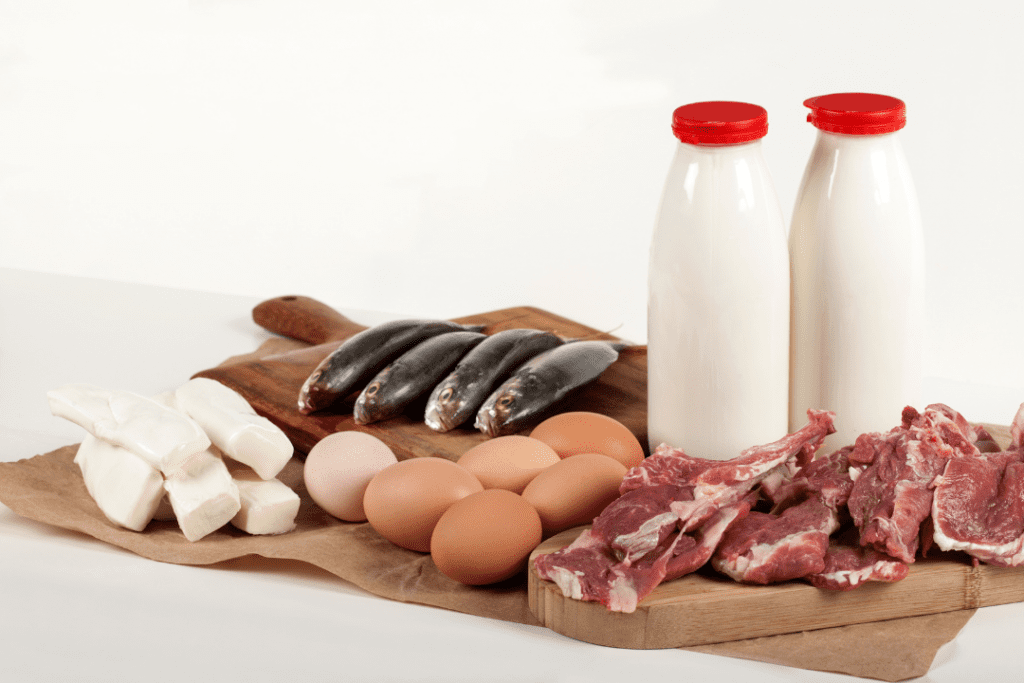

Protein from animals and other sources has the following advantages for an individual’s health:.
Muscle Mass and Strength
Protein obtained from animal sources is perhaps even more effective in muscle building and repair because these proteins are composed of all the essential amino acids. This makes them particularly suitable for usage by athletes and any person in the process of muscle development or with the intention of preserving their muscles.
Bone Health
Animal proteins are beneficial because in them we get vital things like Ca and P for the body and for the bones in particular. Protein and calcium are particularly beneficial to the bones and therefore many foods, such as dairy products, are rich in these nutrients and assist in avoiding osteoporosis and other related bone ailments.
Immune Function
Some form of nutrients like zinc and iron that are prevalent in animal proteins are essential tools that help boost one’s immunity. It goes further to show that these nutrients are important in the production of immune cells, which are fundamental in combating infections as well as diseases.
Energy Levels
Proteins from animals are also dense in energy and assist in regulating blood glucose levels. This is so important, especially for those individuals with an active lifestyle or those that require a steady supply of energy all day long.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability of Plant Protein
Vegetarian and organic diets are usually preferred in the custom as they are thought to cause less harm to the environment. Plant protein production is generally more efficient regarding water and land consumption and also emits fewer greenhouse gases than the animal industry.Perek now turns to a discourse of environmental concerns of animal protein.
Animal farming, particularly extensive animal farming, plays a critical role in environmental problems such as deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. There are significant implications of human diets on the environment, especially the adverse effects or impacts seen above; it is possible to minimize these impacts through reducing animal protein intake in the population’s diet.
Ethical Considerations
Animal Welfare
Avoiding animals as protein sources can be aligned with the ethicist’s worries about animal suffering. Omission or at least the moderation of meat consumption, is generally known to decrease animal suffrage and increase humane approaches to animals.
Human Health
The ethical aspect also applies to human health in relation to the decisions made regarding the consumption of foods. The results revealed that plant-based diets were related to lesser incidences of chronic diseases, which might have a positive impact on the level of health in a society as well as lower healthcare expenditure.
Incorporation of Plant and Animal Protein
Balanced Diet Approach
Introducing plant and animal proteins into one’s diet can prove to be a sensible strategy, taking advantage of the nutrients that both products may contain. A balanced diet gives the assurance that you are receiving all the essential nutrients your body needs.
Flexitarian Diet
A form of eating that is not strictly vegetarian but somewhat limiting in terms of animal proteins is a flexitarian eating plan. This approach can be easily implemented and is compliant with gradual shifting of a diet to a plant-based one without feeling the limitation.
Conclusion
Currently, plant protein vs animal protein are viewed differently, with no one right answer. This depends on the health objectives that one has, the type of diet one would like to take, the moral issues touched by the diet, and the impacts of the diet on the environment. It is, therefore, important to comprehend the various advantages and disadvantages you are bound to encounter when consuming each protein source in order to make intelligent choices that reflect the kind of life you would wish to lead.
FAQs
The major difference in plant protein vs animal protein is that plant protein is an incomplete protein, while animal protein is a complete protein.
How do the keto and Atkins diets work?
Do all proteins from plants provide the body with all the amino acids needed in the diet?
Is the consumption of proteins from plants any better than that from animals?
How do plant proteins contribute to heart health?
Which are some whole plant proteins?








0 Comments