Introduction to Ottoman Empire
During the 15th and 16th centuries, Turkish tribes in Anatolia (Asia Minor) created the Ottoman Empire, and these increased to prominence as one of the most powerful countries in historiography. The rule of the Ottoman Empire continued for more than 600 years and was only replaced in 1922 by the Turkish Republic and its different successor states in the Middle East and Southeast Europe.
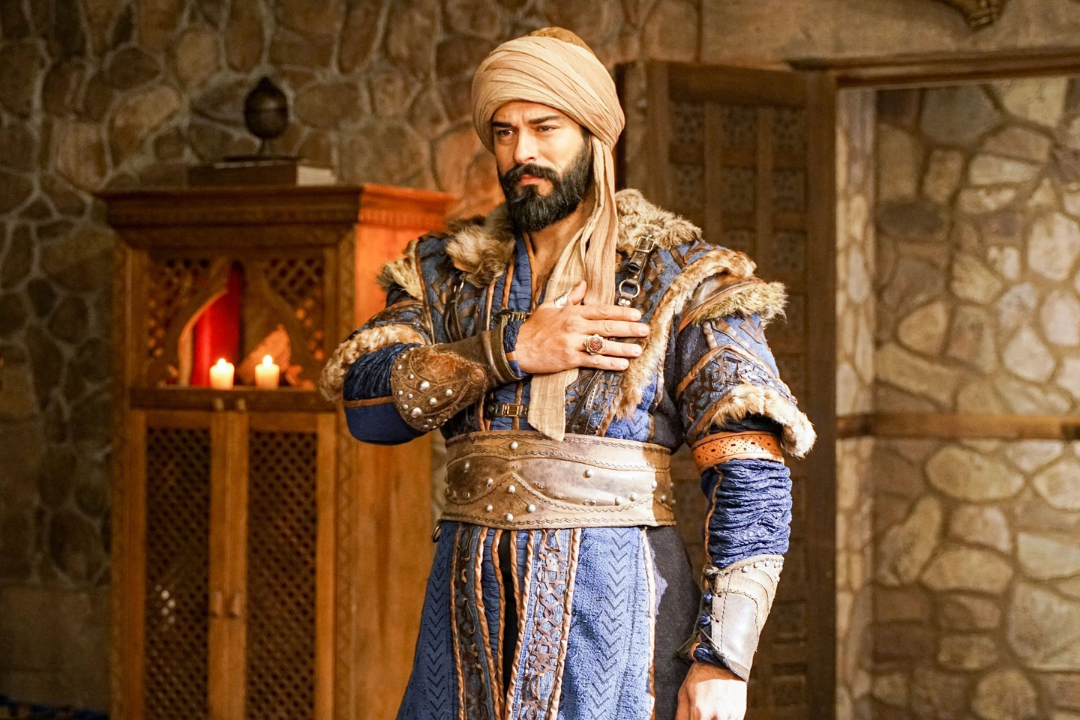

RULER AND FOUNDER OF OTTOMAN EMPIRE
Osman I, the founder of the Ottoman Turkish state, headed across a Turkmen principality in northwest Anatolia compared to regarding 1258 as long as the end of his life in 1324 or 1326. The Arabic form of his name, ʿUthmān, became the starting point for both the dynasty’s name and the name of the empire it established.
The Kayı branch of the Oğuz Turkmen was the heritage of Osman. The capital was founded by his father, Ertugrul, as a principality in Sögüt. Osman commanded the Muslim frontier warriors, designated as the Gazzis, in a slow and determined fight against the Byzantines, who tried to defend their territory in the hinterland of the Asian coastline, all coming from Constantinople (now Istanbul), via Sögüt as their base.
Osman gradually strengthened his power over plenty of former Byzantine territories, like Yenişehir, providing the Ottomans a solid base on which they attacked Bursa and Nicaea (now İznik) in northwest Anatolia. On April 6, 1326, Osman’s son Orhan worked him as ruler of Bursa. In line with Ottoman tradition, Osman slipped out shortly after Bursa was captured, but certain scholars claim that his real establishing happened in 1324, the year of Orhan’s being crowned.
THE BEGINNING OF THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE
The Kayı branch of the Oğuz Turkmen was the origins of Osman. Ertugrul, his father, had established a power base in Söğüt (near Bursa, Turkey). Osman and his army utilized the Seljuq dynasty’s decrease, which had been seriously weakened by the Mongol invasions. At its peak, the Ottoman dynasty ruled in the majority of North Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Europe. The empire’s growth continued for several generations. The foundation for an institutionalized Ottoman state was set up by Osman’s grandson Murad I, and his son Bayezid I executed on the practice.
DESTRUCTION OF THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE
After its defeat in World War I, the Ottoman Empire fell down and was separated. In spite numerous attempts at reform, the empire had already been in decline for centuries, struggling to maintain a centralized administrative structure or an excessive bureaucracy. The rise of more regional interests all over the empire, such as nationalist movements, made the situation more severe. The Ottoman Empire became instantly worked by Turkey once it was forced to breakdown into several distinct territories following its defeat in World War I as just like a result of the Allied powers’ partition agreements and nationalist movements merged.
THE POWER OF THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE
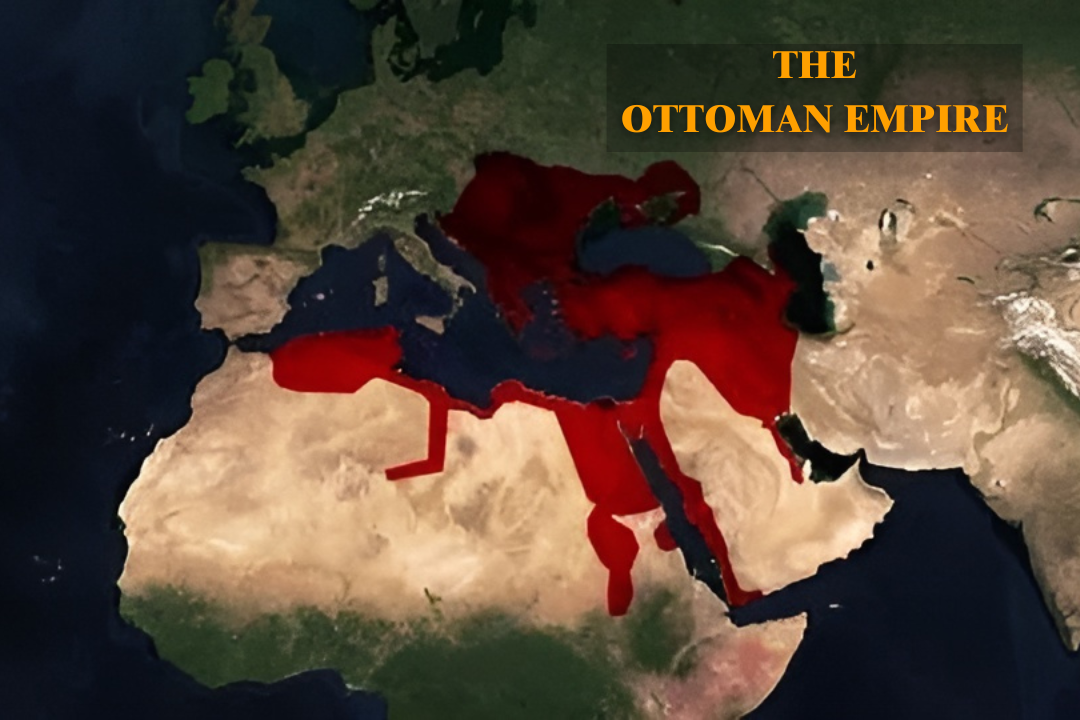
Area Covered by Ottomans:
For several generations, the Ottoman dynasty maintained development. At its height, the empire dealt with most of southeast Europe, including parts of present-day Hungary, Greece, the Balkans, and Ukraine, up to the gates of Vienna; it included large portions of the Arabian Peninsula and portions of the Middle East, which are now controlled by Israel, Egypt, Syria, and Iraq; and it extended as far west as Algeria in North Africa. Osman I (Arabic: ʿUthmān), the nomadic Turkmen leader who built the empire and dynasty approximately 1300, is the origin of the dynastic mention Ottoman. Osman’s grandson Murad I laid the foundation for an institutionalized Ottoman state, continued by Murad’s son Bayezid I.
Fear from Ottoman Army:
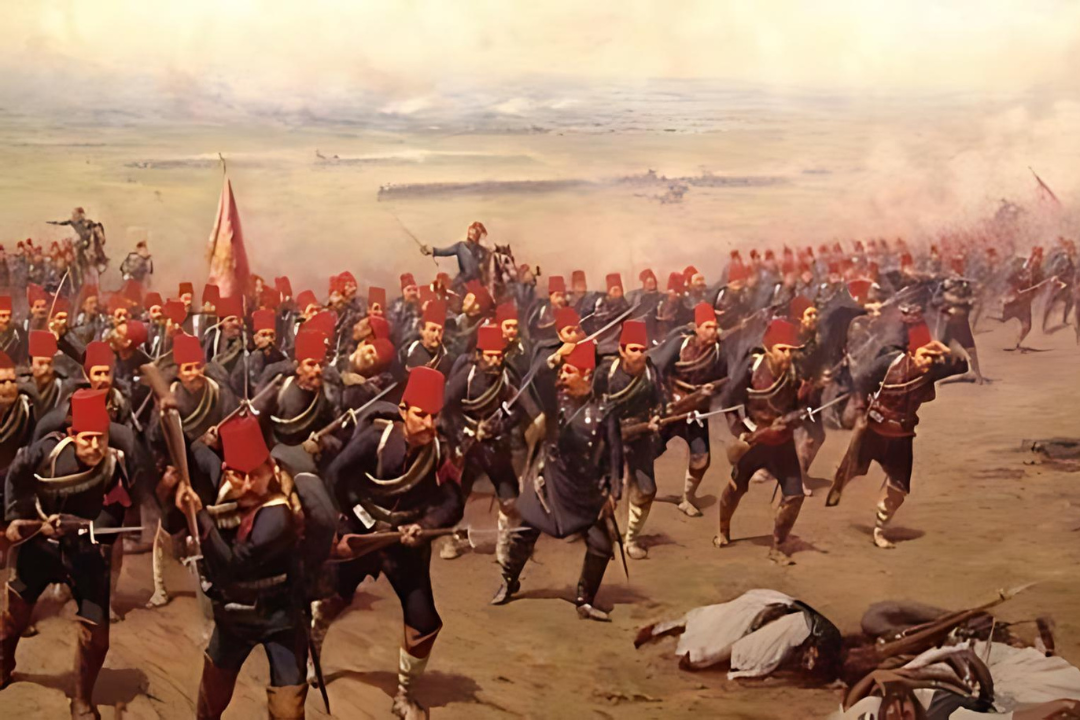
Most Europeans continued to fear that an Islamic-run superpower ruled the Ottoman army as they had two centuries earlier, and, although its ability was reduced, it kept going to be sufficiently strong to prevent the rebels from giving over completely and even to make a few more notable conquests in the East and West.
HOW OTTOMAN EMPIRE MANAGE TO EXIST SO LONG
The longevity of the Ottoman Empire, which lasted for over 600 years (from around 1299 to 1922), can be attributed to several key factors:
Strategic Location:
The empire was situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa, facilitating trade and cultural exchange. This geographic advantage allowed the Ottomans to control important trade routes and gain wealth.
Military Strength:
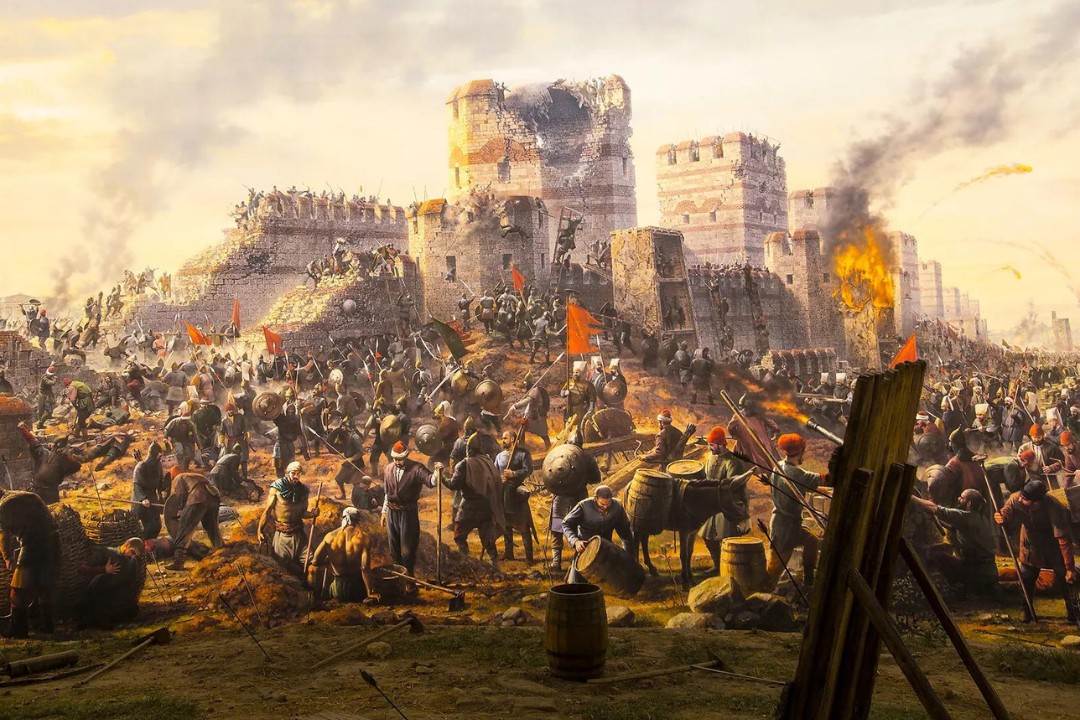
The Ottoman military was highly organized and innovative. The use of gunpowder, particularly cannons, revolutionized warfare and allowed the Ottomans to capture fortified cities, such as Constantinople in 1453. The elite Janissary corps played a crucial role in military success.
Administrative Organization:
The Ottomans developed an effective administrative system that allowed for efficient governance of diverse populations. The millet system enabled various religious and ethnic groups to maintain a degree of autonomy while still under Ottoman rule, fostering loyalty and stability.
Cultural assimilation and tolerance:
The empire was known for its relatively high levels of religious tolerance, especially compared to contemporary European states. This approach allowed for the assimilation of various cultures and reduced the likelihood of rebellion among subjected peoples.
Economic Prosperity:
The Ottomans established a robust economy through trade, agriculture, and taxation. They controlled key trade routes and cities, which contributed to their wealth and allowed for the maintenance of a strong military and bureaucracy.
Diplomacy and Alliances:
The Ottomans skillfully engaged in diplomacy, forming alliances with various states when beneficial. They adapted their foreign policy to changing circumstances, such as forming alliances with European powers during conflicts.
Adaptability and Reform:
Throughout its history, the empire showed a capacity for adaptation and reform. Periodic administrative and military reforms, especially during the Tanzimat period (1839-1876), aimed to modernize the empire and respond to internal and external pressures.
THE MOST POWERFUL SULTAN IN OTTOMAN EMPIRE
Sultan Suleiman I (r. 1520–1566) ascended the throne over 500 years ago. Regardless of getting the longest suffering and arguably the greatest of all Ottoman sultans, Selim “the Grim” had a long and enduring impact on him since the initial days of his reign. Following discovering of his father’s premature passing just eight days earlier, 26-year-old Suleiman showed up at Üsküdar on the Asian side of the Bosporus on September 30, 1520. Due to the Janissaries, Selim’s elite infantry and household troops were highly volatile when it came to political succession; reports of his death were still unknown.
Suleiman crossed the strait the next morning then made the journey to the Topkapı palace, where he was received by the religious and political leaders of the imperial divan (or council), who promised to stand by him. He then followed his father’s funeral cortege through the streets of Istanbul before returning to the Topkapı to complete his accession as the 10th Ottoman sultan.
To read more about these topics, visit our website, www.consumerviews.in and share it with your friends / Follow our Facebook page, Consumerviews India
Nabanna Abhijan Rally: The Unyielding Echoes of 1993 Resurface in 2024











0 Comments