Colour blindness or Coloration blindness, or coloration imaginative and prescient deficiency, can range extensively in kind and severity.
Here’s a detailed observation of the primary kinds and the related troubles they could cause:
Crimson-green coloration; Colour Blindness kinds:
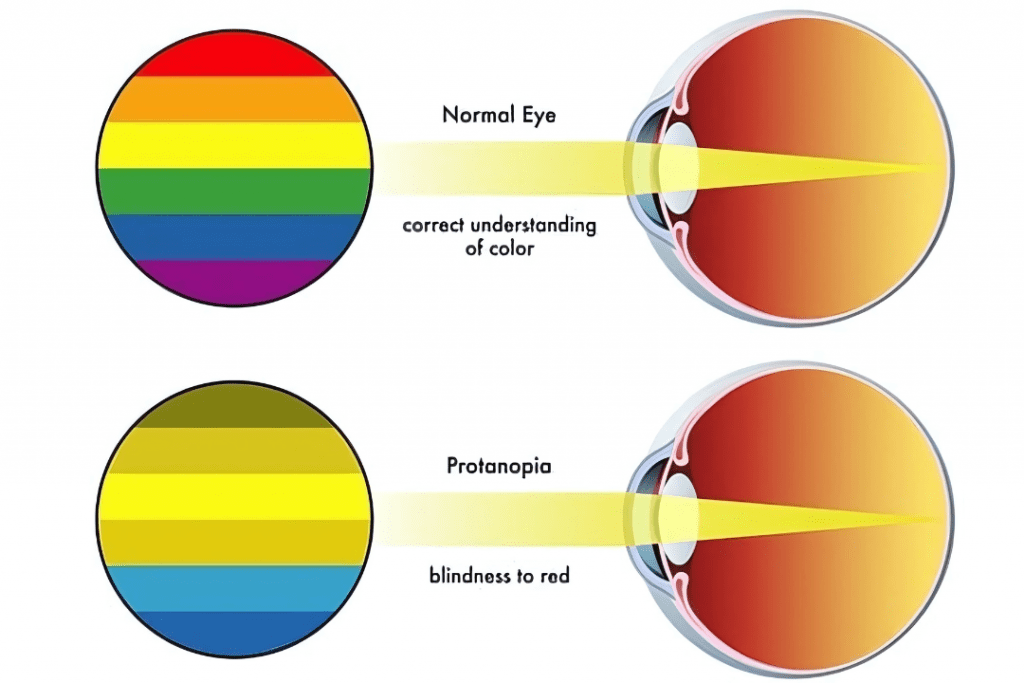
Protanopia: That is a sort of crimson colour blindness wherein the character lacks or has defective crimson cone cells. people with protanopia struggle to distinguish among reds, vegetables, and yellows. crimson may also appear as dark or grayish, and a few reds is probably burdened with vegetables.
Deuteranopia: This includes a deficiency in the green cone cells. people with deuteranopia have issue distinguishing among vegetables and reds, and comparable colorings might appear extra alike.
Troubles: an issue with tasks involving coloration-coded information (e.g., site visitors lights, charts). Demanding situations in activities that rely on color discrimination (e.g., similar clothing, deciding on ripe fruit). capability social and professional affects, including misinterpreting or being misunderstood in color-relevant contexts.
Blue-Yellow coloration; Colour Blindness kinds:

Tritanopia: This circumstance is characterised by a deficiency in the blue cone cells. people with tritanopia have trouble distinguishing among blues and yellows. they might confuse blue with green or gray and yellow with purple or mild gray.
Tritanomaly: That is a much less intense shape wherein the blue cone cells are present but not functioning properly. people have problems in differentiating blue from green and yellow from violet.
Troubles: Issues in identifying and differentiating colorings in positive contexts (e.g., deciding on paint colorings, knowledge coloration-coded facts). viable issues with tasks that contain blue and yellow, including deciphering coloration alerts and labels.
Entire colour Blindness (Achromatopsia) kinds:

Achromatopsia: is an unprecedented circumstance wherein people see the arena in shades of gray because their cone cells do not function properly. it may be entire or partial, with a few people having a limited potential to distinguish among mild and dark; however, there is no coloration notion.
Troubles: Entire reliance on brightness and evaluation instead of coloration for visible information. Giant impact on each day’s activities, as coloration cues are lacking. this will have an effect on everything, from analyzing maps to deciphering environmental cues.
Different kinds Monochromacy: an unprecedented circumstance wherein people have only one sort of cone cell functioning ( commonly rods), leading to very limited coloration notion, normally best differentiating mild and dark.
Dichromacy: Includes having best varieties of functioning cone cells, leading to an extra-limited coloration spectrum in comparison to everyday trichromatic imaginative and prescient.
Popular troubles: Academic and Occupational demanding situations: colour blindness can have an effect on instructional and professional performance, in particular in fields that require specific coloration discrimination (e.g., art, layout, electrical work).
Protection issues: Issue in distinguishing coloration alerts, including site visitors lights and warning signs, can cause protection worries.
Social and Emotional impact: People with colour blindness may also enjoy frustration or self-consciousness, mainly in the event that they experience something unique from others or if their circumstance isn’t well understood by those around them. colour blindness is broadly speaking resulting from genetic elements, although there may be different causes as well.
Here’s a detailed breakdown: causes of colour Blindness
Genetic elements Inheritance sample: Maximum coloration blindness is inherited in a recessive X-connected sample. this means the genes responsible for the most commonplace varieties of coloration blindness ( including crimson-green colour blindness) are placed on the X chromosome. due to the fact that men have one X and one Y chromosome, they’re more likely to have explicit colour blindness in the event that they inherit a defective gene on their unmarried X chromosome. Ladies who have X chromosomes need duplicates of the deficient quality to unequivocally address the situation.
Hereditary Changes: The situation emerges from transformations or cancellations in the qualities that code for the photopigments in the cone cells of the retina. these photopigments are responsible for identifying unique frequencies of light. Mutations in these genes bring about the incapacity to perceive positive colorings as it should be.
Different causes obtained coloration Blindness: Although much less commonplace, colour blindness can broaden later in life due to different factors.
Eye sicknesses: Situations including macular degeneration, glaucoma, or cataracts can have an effect on coloration, both imaginative and prescient.
Neurological situations: Damage to the visible processing areas of the brain (e.g., from stroke or injury) can impair coloration imaginative and prescient.
Medications and chemicals: Positive medications or publicity to chemicals can impact coloration, whether imaginative and prescient, temporarily or permanently. Affected incidence colour blindness influences about eight% of men and zero. 5% of women of Northern European descent. The superiority can range among one-of-a kind ethnic businesses and populations.
Gender variations:
Men: Due to the X-connected inheritance sample, men are extra affected. If a male inherits an X chromosome with the defective gene, he will showcase colour blindness because he doesn’t have another X chromosome to compensate.
Women: Women are much less regularly affected because they might need copies of the defective gene (one on each X chromosome) to expose the circumstance. a female with one defective gene is taken into consideration a provider and normally does not showcase signs.
Circle of relatives history: People with a circle of relatives history of colour blindness are more likely to be affected. If a father has colour blindness, all his daughters can be providers, and his sons can be unaffected ( unless their mom is a provider).
Genetic testing: Hereditary testing can confirm the presence of transformations in the hue’s creative and judicious qualities and anticipate the likelihood of passing the situation to posterity. this will be basically helpful for information the danger in fate.
Influence on individuals apparent idea: Those impacted may likewise disapprove of assignments that depend on distinctive colorings, including unraveling hue-coded data or settling on reasonable colorings in assorted settings.
Every day ways of life: The effect on every day ways of life differs depending upon the seriousness and kind of shading visual deficiency. A few people may also adapt nicely by using non-coloration cues or eras designed to make useful resource coloration imaginative and prescient.
Emotional and Social components: People with colour blindness might enjoy frustration or socially demanding situations, mainly if their circumstance are misunderstood or if it influence their professional or non-public lifestyles. knowledge these genetic and different elements can help in presenting suitable assistance and accommodations for people with colour blindness.








0 Comments