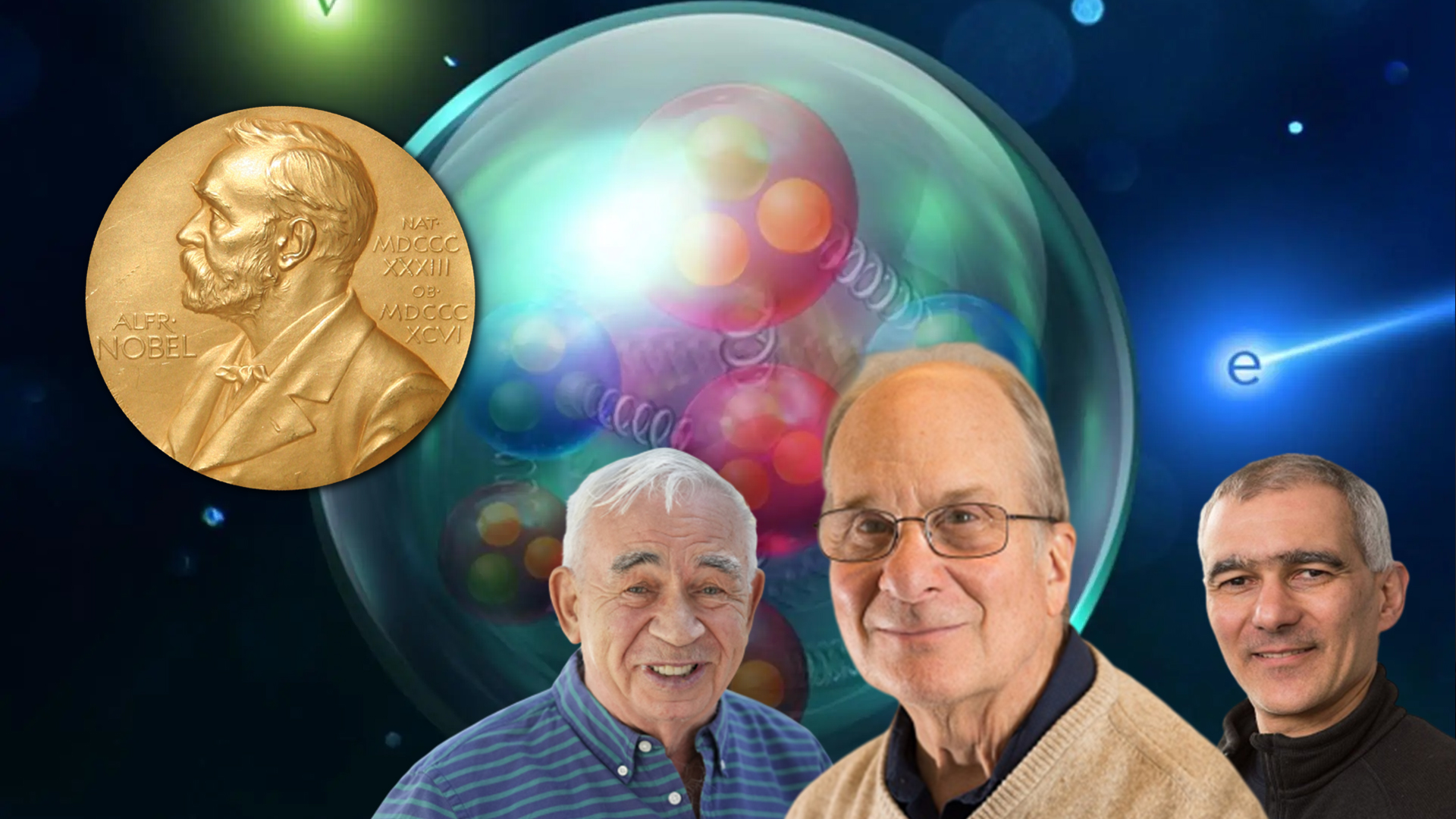
Every once in a while, a finding in the fascinating realm of science and discovery changes how we perceive the universe and how we relate to it. For their groundbreaking work in the field of nanotechnology, Moungi Bawendi, Louis Brus, and Alexei Ekimov received the 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. With the development and production of quantum dots, minuscule particles with amazing characteristics that have found uses in everything from television screens to cancer surgery, these visionaries have shed light on the nanoworld.
A Journey into the Nanoworld
The nanoworld is a place where the fundamental principles of physics appear to bend and stretch, giving reality a fantastical appearance that borders on enchantment. It is a realm where quantum effects rule supremely and matter is measured in millionths of a millimetre. It’s a universe that tests our instincts and entices us to delve deeper into its secrets.
Early in the 1980s, Moungi Bawendi, Louis Brus, and Alexei Ekimov individually set out on this path and discovered quantum dots—nanoparticles so minute that quantum effects control their characteristics. The size of the particles is the most important factor in this quantum wonderland. By controlling these elusive quantum phenomena, Ekimov, Brus, and Bawendi ushered in a new age of nanotechnology.
Quantum Dots: The Marvelous Crystals
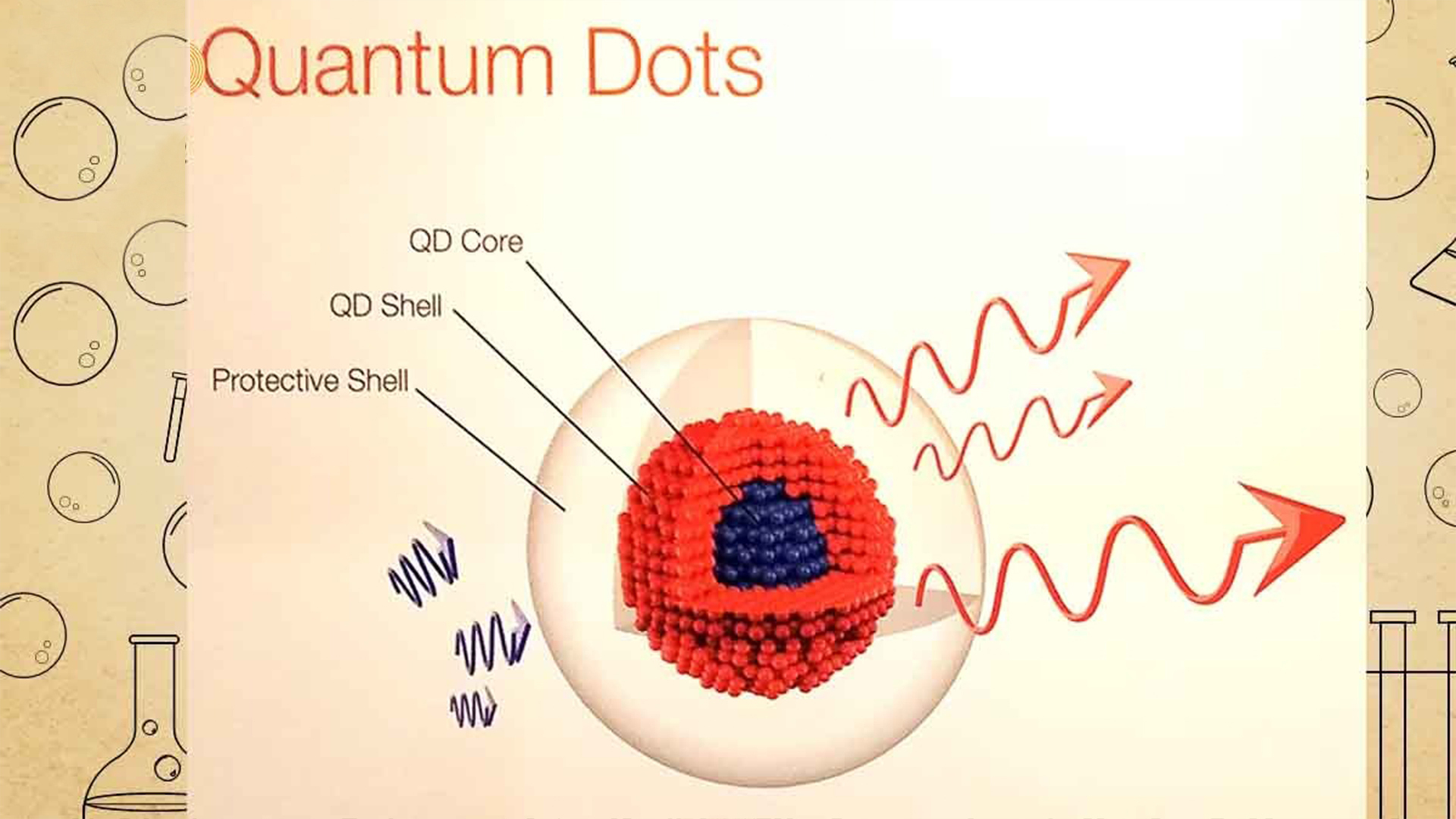
It’s not your normal crystal, the quantum dots. In actuality, they are nanometer-sized crystals with extraordinary optical qualities. Understanding the strange realm of quantum physics is necessary to fully appreciate their significance. There is less room for electrons, which are both waves and particles when particles get very tiny. The characteristics of the material are dramatically altered as a result of the close proximity of these electrons.
The introduction of quantum dots occurred in this setting. In their respective labs, Ekimov and Brus showed that the size of these quantum dots affected the light wavelengths that they absorbed. A size-dependent quantum effect was possible because smaller dots were able to absorb more blue light. This discovery was nothing short of revolutionary, as it expanded our understanding of how materials behave at the nanoscale.
Quantum Dots: A Third Dimension for Chemistry
Imagine the periodic table adding a third dimension, where an element’s characteristics are now influenced by its nanoscale size as well as its atomic structure. By adjusting the size of quantum dots, scientists were now able to create totally new types of materials. The potential for invention looked limitless at this point, and scientists were eager to delve into this new region.
But there was a problem: the created quantum dots were frequently afflicted by flaws and size fluctuation. The third Nobel Prize winner, MoungiBawendi, set out to overcome this obstacle. His unwavering quest for excellence resulted in a paradigm-shifting discovery in 1993. By carefully regulating the solution’s temperature, Bawendi and his team have created a technique for growing nanocrystals of a certain size. The quantum effects displayed by these almost flawless nanocrystals were unique, paving the way for the broad application of quantum dots in nanotechnology.
Quantum Dots in Our Everyday Lives

Today, quantum dots are pervasive and have a subtle impact on how we conduct our lives. They are the bright stars that are hidden behind the monitors on our computers and televisions, and they are essential to QLED technology. Blue light is converted into vivid colours that appear to dance before our eyes by quantum dots. They also improve the light that comes from some LED bulbs, producing settings that may be both energising and soothing.
However, quantum dots have applications well beyond just illumination and entertainment. They are used by biochemists to map the complex terrains of cells and organs, and by clinicians to track tumour tissues within the human body. Chemists use their catalytic abilities to fuel chemical processes, creating new avenues for chemistry research.
Moungi Bawendi, Louis Brus, and Alexei Ekimov received the 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry in recognition of their outstanding contributions to the field of nanotechnology through the discovery and development of quantum dots. These little, enchanted particles have moved beyond science fiction and are now a crucial component of our daily existence. Quantum dots continue to light the way to brand-new vistas in science and technology, from the displays that enthral us to the medical advancements that save lives. We can only speculate about what additional adventures are waiting to be discovered by the future generation of scientists and inventors as we continue to solve the secrets of the nanoworld.







0 Comments