Introduction
A rapid worldwide evolution of wireless communication technology happens today because people require better internet performance and speed in their digital networks. So, what is the future of Internet Connectivity?
Hello readers! This is Sourav; In this article we are going to discuss about The Future of Internet Connectivity. I encourage you to read the full article for a deeper understanding. Also, feel free to leave a comment below and let me know your thoughts.
The deployment of 5G networks throughout the world shows the way to forthcoming 6G systems that will reshape industry operations and economic sectors and fundamental human connection to the internet. The paper examines wireless communication progress from previous technology generations while discussing 5G characteristics and 6G projected features that will redefine our digital society.
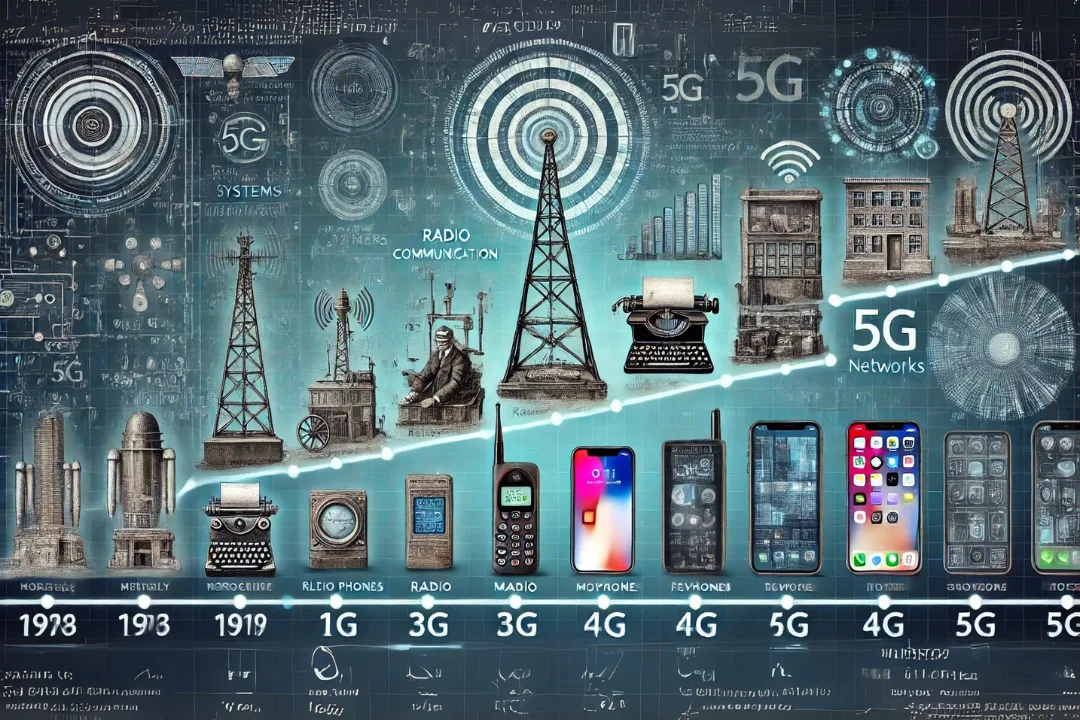
The Evolution of Wireless Communication
- Since 1G arrived in the 1980s wireless mobile networks have successively delivered immense transformations to their technology.
- The wireless communication industry introduced analog voice calls with restricted data transfer capabilities that operated during the 1980s.
- 2G (1990s): Digital voice transmission, SMS, and basic mobile data services.
- The 2000s introduced mobile internet services while adding multimedia communications and video telephony features to the 3G networks.
- The 2010s brought 4G which supplied fast mobile broadband capability for streaming videos and conducting online games.
- 5G (2020s): Ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and massive device connectivity.
Each generation has sequentially developed the fundamental concepts by creating new applications which push forward industrial development. Currently researchers and engineers are dedicating efforts to develop 6G which would surpass the existing technological boundaries.
5G: The Present and Its Capabilities
The fifth generation wireless network known as 5G constitutes a major advancement in mobile communication technology. Key features of 5G include:
1. Enhanced Speed and Capacity
The 5G network technology provides speeds reaching 10 Gbps which represents 100 times greater speed than 4G LTE. Users can obtain 4K and 8K video streaming and real-time gaming and download files at ultra-speeds through this network.
2. Low Latency
Data transmission speed through 5G networks becomes as short as 1 millisecond.
3. Massive IoT Connectivity
The infrastructure of 5G allows a million devices to connect within each square kilometer thus establishing itself as an optimal solution for smart cities and industrial automation and large-scale Internet of Things implementations.
4. Network Slicing
Through network slicing technology operators can establish various virtual network domains on singular physical networks to optimize the connectivity of their different operational fields including healthcare and automotive as well as entertainment applications.
5. Energy Efficiency
The power efficiency of 5G networks improves data transmission efficiency because they employ lower energy consumption for each transmitted bit. Sustainable development alongside extended battery usage occurs with this technology.
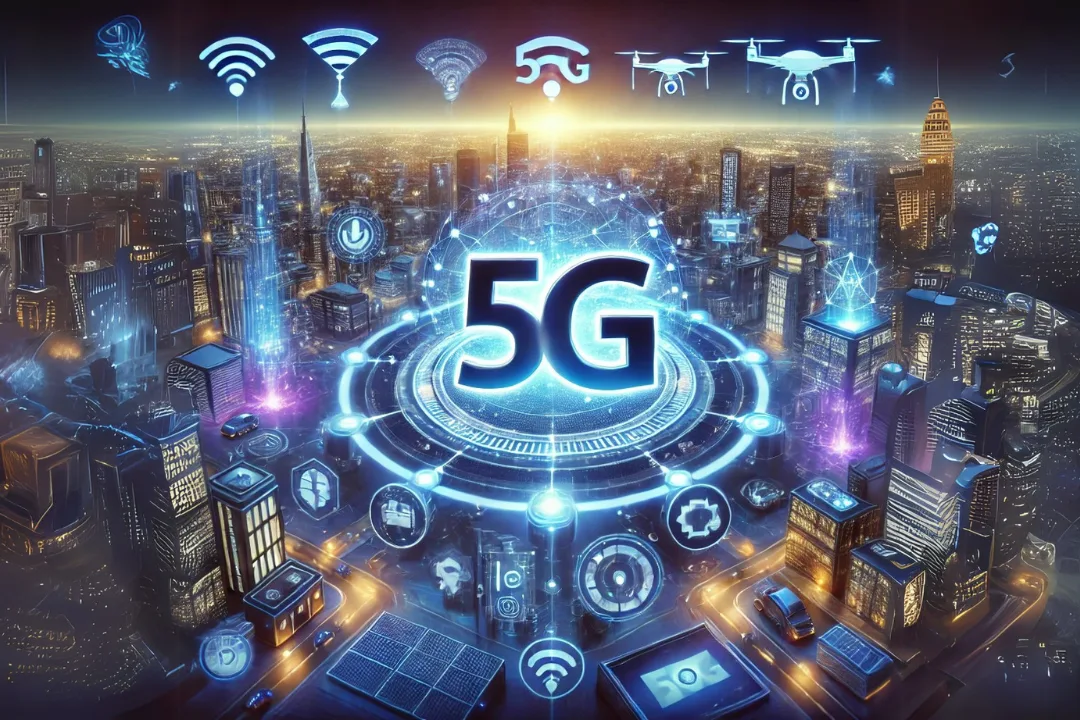
6G: The Future of Connectivity
The ongoing research into 6G has started before 5G’s full deployment while developers expect its implementation to occur during the 2030s.
1. Unprecedented Speeds
6G seeks to deliver data at rates reaching 1 terabit per second which can minimize transmission delays to bare minimum. Holographic communication at high resolution together with fully integrated AR/VR systems and instant cloud processing capabilities will become possible through 6G network deployments.
2. Ultra-Low Latency
Fast 6G networks will run data at microsecond levels which will enable instant-first applications to operate across robotics systems and artificial intelligence systems and space probes.
3. AI-Driven Networks
The management of 6G networks through artificial intelligence (AI) techniques will focus on both performance enhancement and predictive failure systems and security improvement protocols.
4. Integration of Terahertz (THz) Frequencies
The terahertz spectrum (0.1-10 THz) which 6G will adopt enables enormous data transfer capabilities that support high-precision applications including advanced imaging techniques and sensing operations.
5. Advanced IoT and Smart Environments
6G technology will create the conditions for smart city infrastructure and automated industrial operations while developing real-time data exchange capabilities for future healthcare solutions.
6. Quantum Communication and Security
6G technology will include quantum computing elements that deliver quantum-based encryption which guarantees strong network security.
Impact on Various Industries
The development of 5G and 6G technology creates extensive transformative effects within different industrial sectors:
1. Healthcare
- Remote surgeries with real-time precision.
- AI-powered diagnostics and patient monitoring.
- Smart hospitals with interconnected devices.
2. Automotive and Transportation
- Autonomous vehicles with improved safety and navigation.
- Smart traffic management reducing congestion.
- Enhanced vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication.
3. Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
- Industrial automation with AI-driven robots.
- Predictive maintenance reducing downtime.
- Augmented reality (AR) for training and troubleshooting.
4. Education and Workforce
- Immersive virtual classrooms and training.
- AI-assisted learning and skill development.
- Remote collaboration with high-fidelity experiences.
5. Entertainment and Media
- Ultra-high-definition (UHD) streaming and gaming.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences.
- Interactive and AI-driven content creation.
Challenges and Considerations
The potential benefits of 5G and 6G systems come together with multiple implementation barriers.
1. Infrastructure Deployment
The deployment of 5G networks alongside 6G systems demands big spending on building network infrastructure through use of fiber optics and small cells and base stations.
2. Spectrum Availability
Real spectrum management plays a vital role in preventing overlapping signals between wireless technologies during operation.
3. Security and Privacy
The growing scope of connectivity leads to rising cybersecurity threats in the network. Advanced encryption technologies alongside AI-driven security solutions should be considered mandatory.
4. Energy Consumption
The massive rise in data transfer will require sustainable energy solutions since efficiency gains cannot address the increasing power consumption.
5. Regulatory and Ethical Concerns
Regulatory bodies along with governments need to implement policy frameworks which protect fair network usage and prevent digital divide formation and defend data privacy and Artificial Intelligence ethical standards.
Conclusion
The future of internet connectivity due to 5G and subsequent 6G technologies will completely reshape communication methods while changing both professional operations and our relationship with technological systems. 5G accelerates remarkable transformations yet 6G technology advances beyond that by developing a hyper-connected environment with maximized speed and intelligence and efficiency levels. To exploit the complete potential of these next-generation networks it becomes necessary to resolve issues with infrastructure and security and resolve ethical matters. Both 5G and 6G systems will form the foundation of digital transformation as we build a smarter interconnected future because they enable limitless innovations for progress.
So, this is all for now, we’d love to hear from you. Feel free to share your suggestions or questions in the comments below. let me know your thought about The Future of internet connectivity, and don’t forget to share them with friends and others who might benefit! Save Consumerviews.in your bookmark for easy access, and follow our Facebook Page Consumerviews India for more articles like this.











0 Comments